The Basilica of San Paolo, located in Rome, Italy, is a magnificent structure that bears witness to centuries of history, intricate architectural design, and profound religious significance. As one of the four major basilicas of the Eternal City, it stands as a testament to the enduring legacy of Christianity and the cultural wealth of Rome. This article delves into the history, architecture, and religious importance of the Basilica of San Paolo, offering a comprehensive understanding of this iconic monument.
Historical Overview:
The history of the Basilica of San Paolo traces back to the early days of Christianity. It was erected on the burial site of Saint Paul the Apostle, whose martyrdom in the 1st century AD marked a pivotal moment in the spread of Christianity. The original church, built in the 4th century by Emperor Constantine, was a testament to the veneration of Saint Paul’s relics. However, it suffered multiple damages and reconstructions over the centuries due to fires, invasions, and structural challenges.
Architectural Marvel:
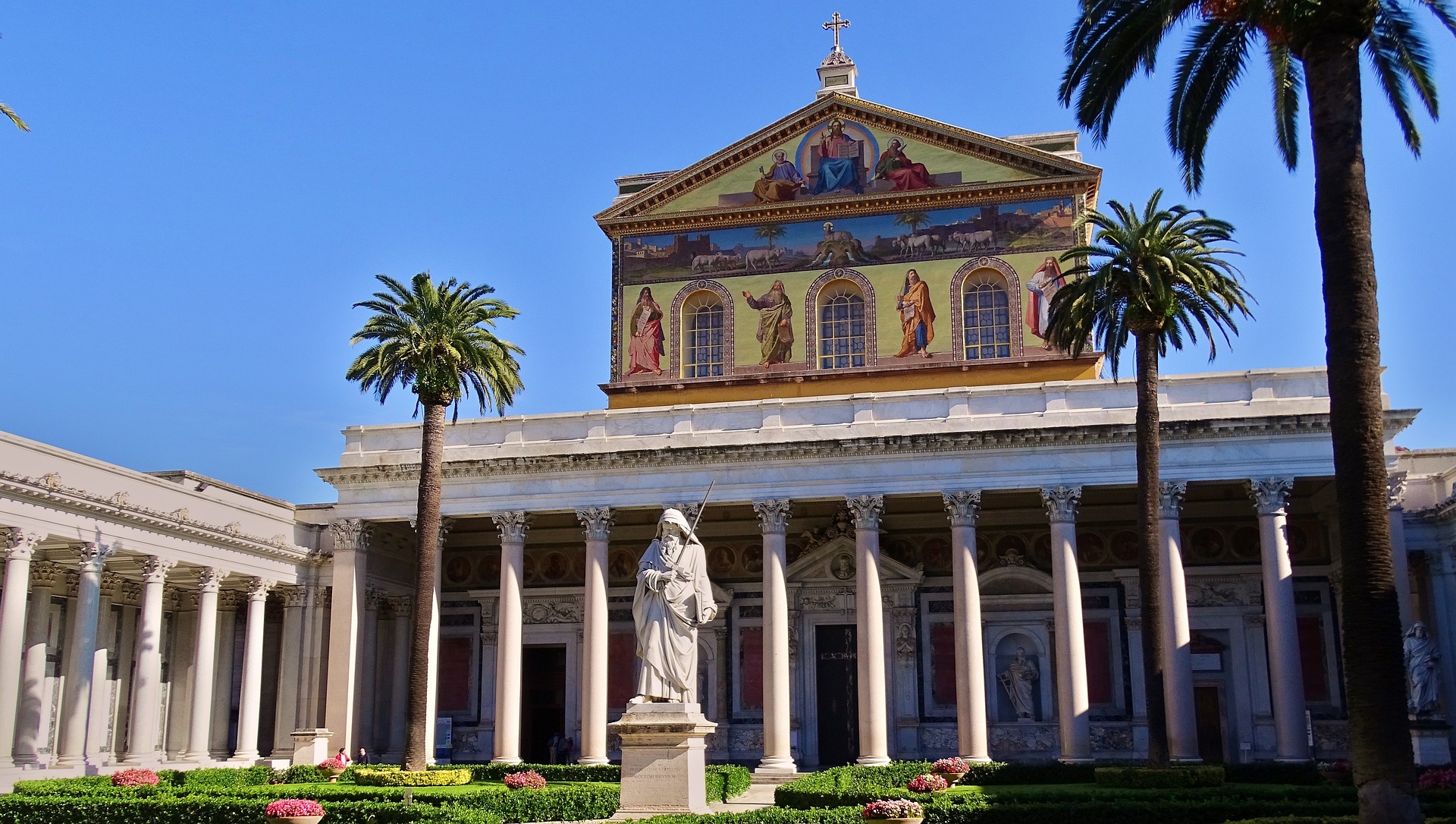
The architectural evolution of the Basilica of San Paolo is a captivating journey through different eras and styles. The current structure, consecrated in 1854, is the result of a remarkable reconstruction led by various architects. Its grandeur is evident in its Latin cross plan with five aisles, stunning mosaics, and an impressive central nave. The facade, characterized by a monumental portico and intricate decorative elements, showcases a harmonious blend of Romanesque, Gothic, and Neoclassical influences.
The basilica’s interior boasts awe-inspiring artwork and architectural elements. The intricate apse mosaic, depicting the “Conversion of St. Paul,” is a breathtaking masterpiece that narrates the pivotal moment of Paul’s life. Additionally, the coffered ceiling, adorned with intricate designs and frescoes, exemplifies the level of craftsmanship present in the basilica.
Religious Significance:
The Basilica of San Paolo holds profound religious significance within the Catholic faith. As the burial place of Saint Paul, it is considered a sacred pilgrimage site for believers from around the world. The basilica’s role in fostering ecumenism and dialogue among different Christian denominations is noteworthy, as it symbolizes the shared heritage and teachings of Christianity.
The basilica also hosts various religious ceremonies, including liturgical celebrations and Papal Masses. Its spiritual aura and historical context make it a site of reflection and prayer for both pilgrims and visitors alike.
Cultural and Artistic Treasures:
The interior of the Basilica of San Paolo is adorned with a treasure trove of artistic and cultural gems. The intricate frescoes, sculptures, and mosaics that embellish the walls and ceilings pay homage to the artistic achievements of various periods. Notable works include the statue of Saint Paul by Arnolfo di Cambio, the stunning medieval cloister, and the portraits of the popes adorning the nave.
Restorations and Preservation:
Throughout its history, the Basilica of San Paolo has undergone numerous restorations to preserve its architectural integrity and artistic heritage. Notably, the fire of 1823 inflicted substantial damage, prompting a large-scale restoration project that aimed to recreate the basilica’s former glory. These restoration efforts continue to be vital in maintaining the basilica’s structural stability and artistic beauty.
The Basilica of San Paolo in Rome stands as an enduring symbol of faith, culture, and history. Its majestic architecture, rich religious significance, and artistic treasures make it a must-visit destination for pilgrims, art enthusiasts, and history buffs. As a testament to the enduring legacy of Christianity and the cultural richness of Rome, the Basilica of San Paolo continues to inspire awe and reverence in all who have the privilege to experience its splendor.